This article applies to Exalate Classic only. For New Exalate, refer to this documentation.
Let's discuss a use case where you need to sync between Jira cloud and Jira on-premise instances, where the Jira on-premise instance is behind the firewall and is not accessible from the outside network.
Why Sync Public and Private Jira Instances?
Often, customers for security reasons want to keep their instances behind a firewall, yet synchronize data with a public-facing Jira cloud instance. Such a setup allows the users working in Jira on-premise to maintain privacy and compliance, while getting the benefits of an integration.
In such a manner, teams can maintain transparency with their external partners, customers, or suppliers, boosting trust without exposing internal workflows.
Such a synchronization helps enforce data governance, ensuring only approved information crosses between instances, meeting security and compliance needs.
Using Exalate to Sync Between Private Jira On-premise to Jira Cloud Instances
The Exalate App is able to handle this type of communication between instances and synchronize issues either in a uni- or bi-directional manner.
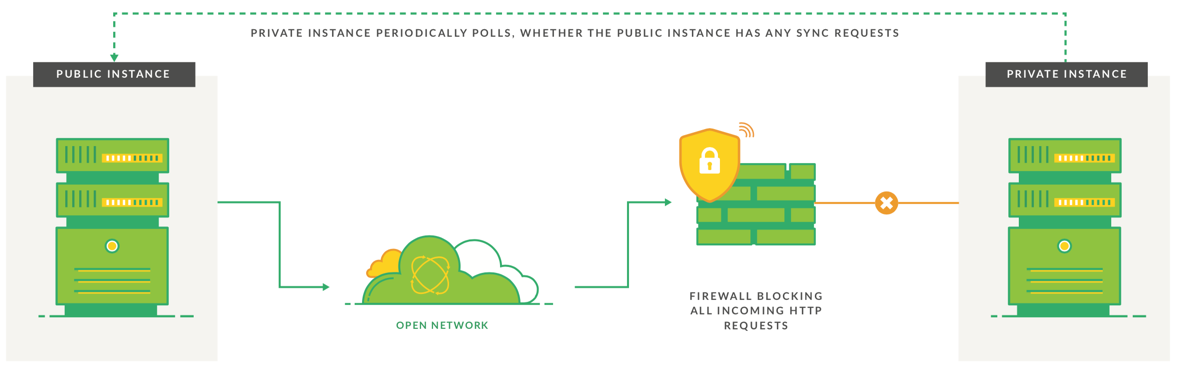
In such cases, only the private instance can initiate the network traffic to the public one. With the help of the Exalate app, you can sync issues between instances even if one of them is not accessible from the public network.
How is the traffic different between public and private instances?
Example
You have two Jira instances. One is a private instance (is not accessible from the outside network) and the other is a public instance.
Let's call the private instance Internal and the public instance External. Only the Internal instance can initiate network traffic to the External instance.
You want to exchange data between the InternalProject and ExternalProject that are present on the internal and external Jira instances respectively.
Sync Public and Private Jira On-premise Instances
Another common use case is synchronization between 2 Jira on-premise instances, where one Instance is behind the firewall and is not accessible from the outside network. The Exalate is able to handle this situation by configuring a 'private' to 'public' connection. Only the private instance initiates the network traffic to the public one and requests if there are any changes queued.
Sync Between Two Private Jira Instances
Using Exalate, it is also possible to sync between two private Jira instances.
For more information, please read how the traffic is different between public and private instances.
Example
You have two Jira instances. One instance is behind a firewall and you cannot access it from your side. Another instance is a public instance which can be accessed from the public network. Let's call the private instance Internal and the public instance External. Only the Internal instance can initiate network traffic to the External instance.
You want to exchange data between the InternalProject and ExternalProject that are present on the internal and external Jira instances respectively. Below you can see the configuration steps to set up such a kind of synchronization.
Below you can see the configuration steps to set up the synchronization.
Configuration Steps
- Set up a Connection from the External Instance.
- Click 'I don't have a URL'.
Exalate suggests available connection types based on the destination instance's version of Exalate. - Select the proper connection type as shown below
You can choose between Basic or Script configuration modes, since Visual configuration is only allowed in Public connections.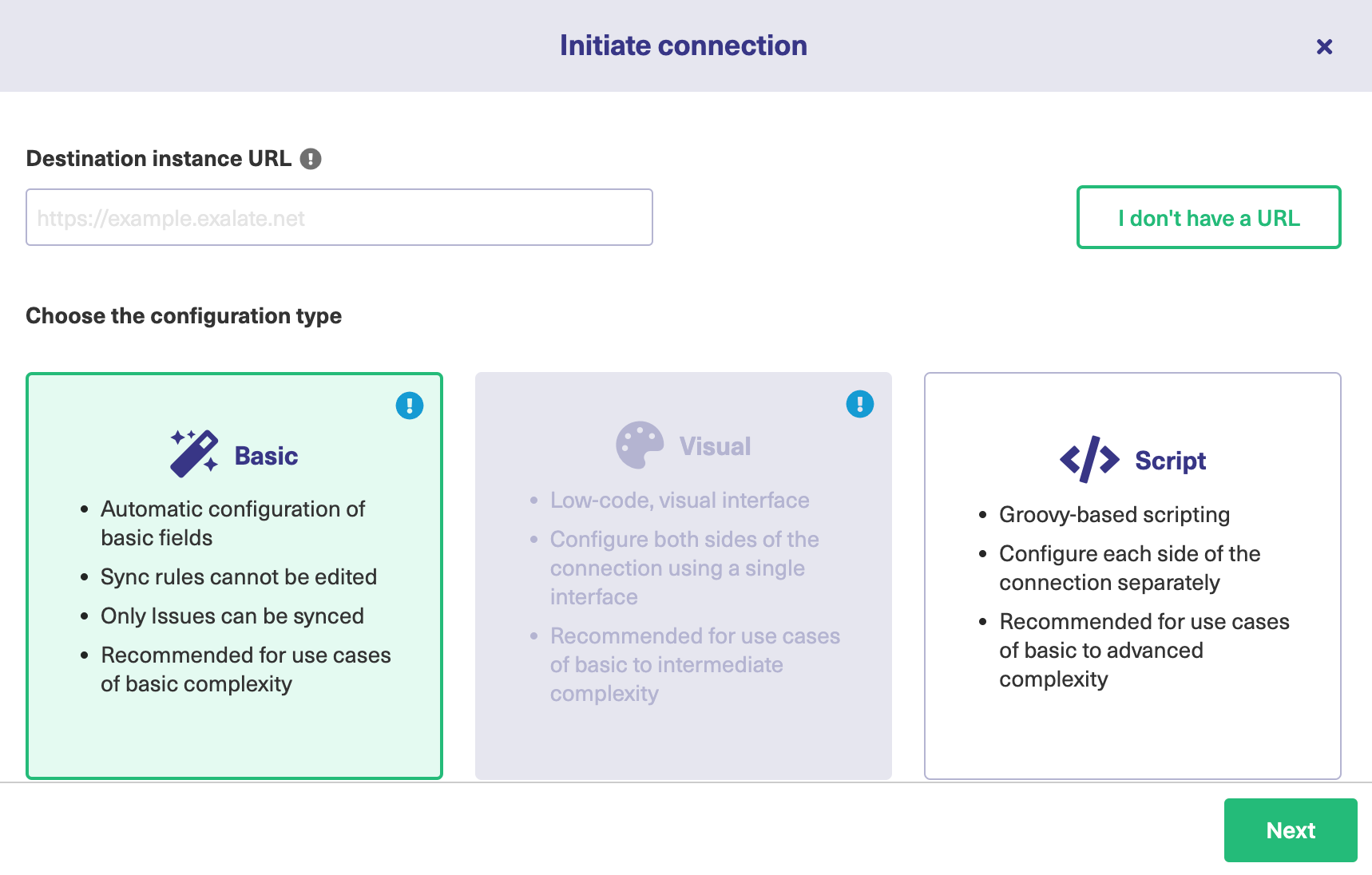
- Complete other steps from the connection wizard.
- Click 'I don't have a URL'.
- Send an Invitation to the Destination Instance.
- Make sure the Destination side has accepted the invitation.
- Synchronize issues.
For more information, please read the getting started guide.
