This article describes what a replica is and how it is used in the synchronization process.
Note: For a better understanding of the process involving sync rules, please refer to this article on sync rules.
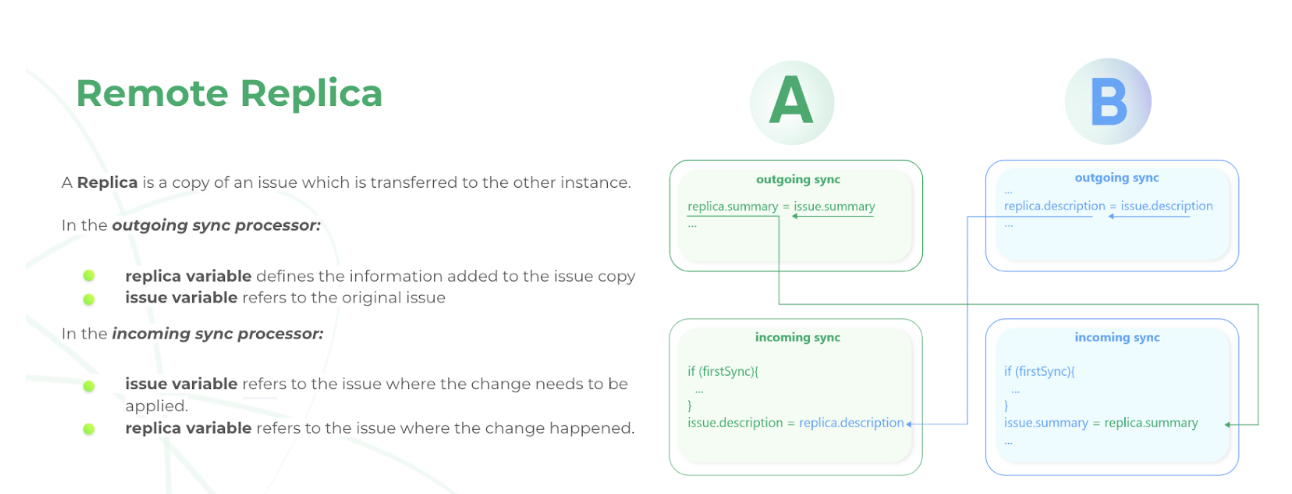
A replica is a copy of the information that is getting transferred to the destination side. Exalate uses replicas to extract specific data and then send it over. You can use the replica in the Outgoing rules to specify which data should be sent. On the destination side, the replica object is used to represent the remote issue. It contains only the fields provided through the data filter on the source side.
You can view the replica details in the Entity Sync status panel. If the entity is synced, you can view the local replica by clicking the Show local replica button and the remote replica by clicking the Show remote replica button.
The replica looks something like this:

In this way, you can see what information is being passed over from the local instance. The remote replica has a similar structure.
Note: The hubIssue represents the information that is passed and how you can access it. Whereas, the replica is more than the hubIssue section. The replica is the entire payload to be transferred between platforms.
Note: For more information, please see the section on The Synchronization Process Step-by-Step here.