This article applies to Exalate Classic only. For New Exalate, refer to this documentation.
Configure the Sync Scope
1. Click Configure Sync to start configuring the connection.

You can also configure an existing connection by navigating to the Connections tab in the Exalate Admin console. Then click the Edit Connection ![]() icon in front of the Connection name.
icon in front of the Connection name.
2. Select Project on both sides. (if applicable).
Select the projects you want to use for the Connection, at both ends.

3. Click Filter entities (Optional).
With this option, you can decide what information must be synchronized.

Note: If no option is selected, all the entities will be synced by default.
Set the Filters
Select the appropriate filter you want from the list. For instance, for Jira, you can choose to sync all Bugs, Tasks that have a label = 'totest'.
Filters for Jira:
You can also choose to have multiple filter options.
Example 1:
|
In this case, the Priority filter has 2 options. The options you select are considered as an OR operation, High OR Low.
With 2 different filter types, Issue type and Priority, the options you select are considered as an AND operation.
So, there are 2 possible combinations for the above sync:
- Bug with High priority AND Open status,
- Bug with the Medium priority AND Open status.
Example 2:
If there are no options selected for the Issue type, like in the example below:
|
All issue types with the Priority High OR Medium and status Open are synced.
4. Set the Sync Method

This option allows you to decide how information must be synced between the task management systems. You can choose from the following options:
- Manual: The issue is synchronized manually.
- Automatic: The issue is synchronized automatically based on the entities you have filtered in the previous step.
- Disabled: The synchronization is disabled.
The arrows decide the direction of the synchronization.
5. Click Next to configure the field mappings.
Add the Field Mappings (Rules)
Rules denote the mapping between different entities & decide what must be synchronized. There are predefined default mappings for basic fields in every Visual mode Connection.
You can access these mappings by clicking Next after configuring the sync. The Rules section consists of these mappings.

Note: The above is just an example of mapping. The actual mappings will depend on the platforms under sync.
The top bar displays the local instance's short name and the remote instance's short name. These are the names you provided while setting up a connection.
It also has a Sync direction. The arrows indicate the direction, whether uni or bi-directional. You can choose to Expand all or Collapse all the mappings.
You can Edit connection ![]() or Delete mapping . You can also drag and drop them, up or down to re-prioritize.
or Delete mapping . You can also drag and drop them, up or down to re-prioritize.
Edit Mappings
To edit mapping click the Edit mapping ![]() icon.
icon.
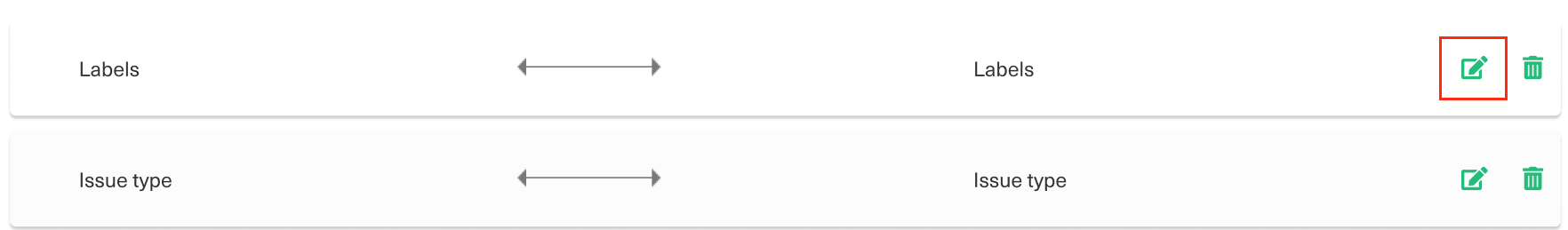
An Edit mapping dialog box opens.

Select the new fields to be mapped on both sides from the drop-down list. You can also edit the Sync direction. Sync direction allows you to control your sync in a specific direction, indicated by the arrows.
Click Save to apply the changes.
Delete Mappings
You can delete a specific mapping if you don't want it.
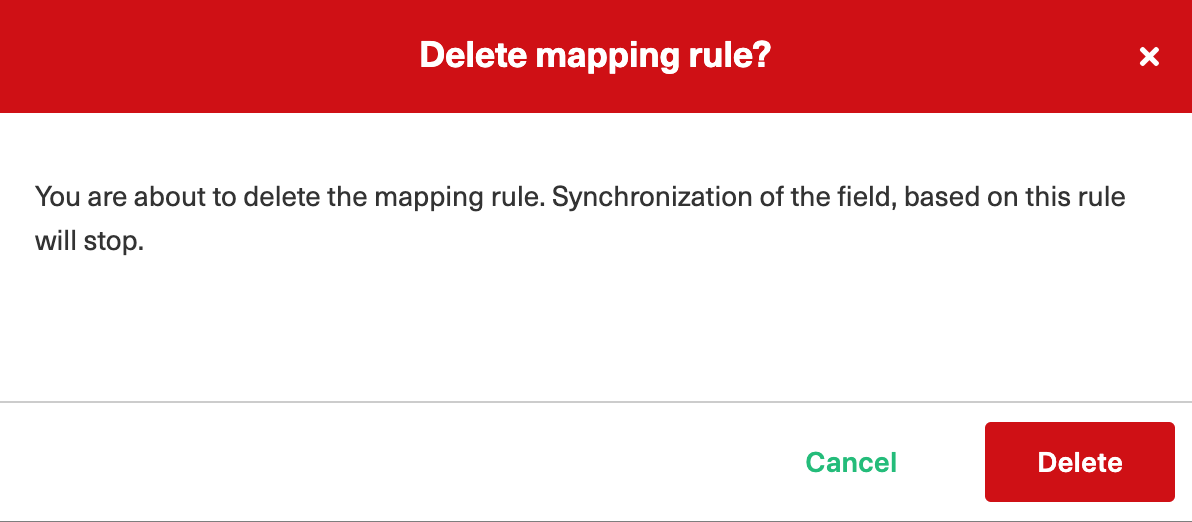
Clicking the trash icon opens up a prompt to confirm you want to delete the mapping. Click Delete to confirm the deletion.
Add New Mappings
To add a new mapping, click the Add mapping button.
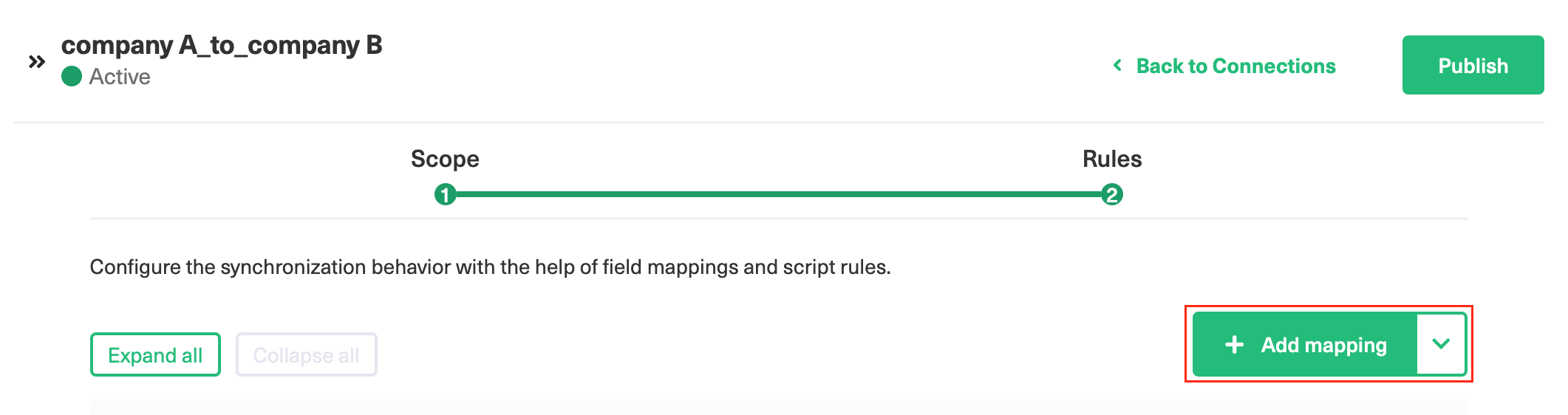
An Add mapping dialog box opens.
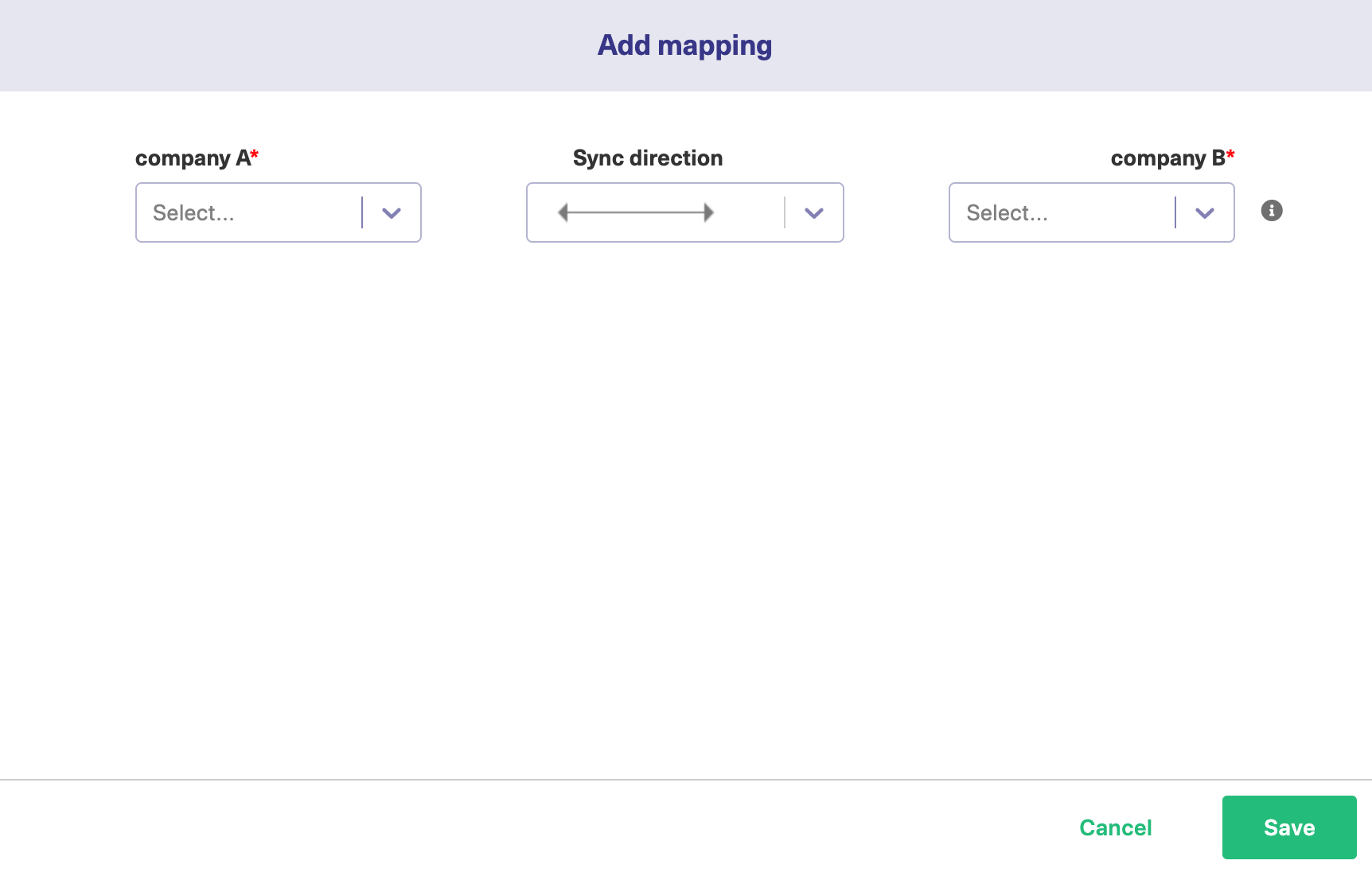
Select the required fields at both ends from a drop-down list. You can choose to keep the Sync direction as it is by default or edit it. Sync direction allows you to control your sync in a specific direction, where the arrows indicate the direction.
You can add sub-mappings by clicking the plus icon.
You can also specify what to do if the selected values do not match.

If no matching value is found you can choose to:
Option |
If the value doesn't exist |
|---|---|
Set a default value |
Fields are set to a default value you specify |
Report an error |
An error appears & is displayed on the Errors tab. The synchronization is blocked in this case. |
Do nothing |
The values stay the same |
Save the changes when done.
Custom field mappings
When you set up a Visual mode connection, Exalate fetches some of the custom fields for you. These are available through a drop-down list while adding a mapping.
If you don't find the custom field, there is always an option to add Scripts.
The following are the supported custom field types:
Text:
- Jira Cloud: Text Field (multi-line), Text Field (single line)
- ADO: Text (single line), Text (multiple lines)
- Zendesk: Text, Multi-line, Date, Number, Decimal
Option:
- Jira Cloud: Radio Buttons, Select List (single choice)
- ADO: Picklist (string), Picklist (integer)
- Zendesk: Drop-down
User:
- Jira Cloud, on-prem: User Picker (single user)
- ADO: Identity
- Zendesk: - Not supported
Add Scripts for Advanced Configuration (Optional)
For advanced synchronization use cases, you can add Groovy Scripts to your Visual mode Connection.
To do so, click the arrow on the Add Mapping button. Select Add Script.

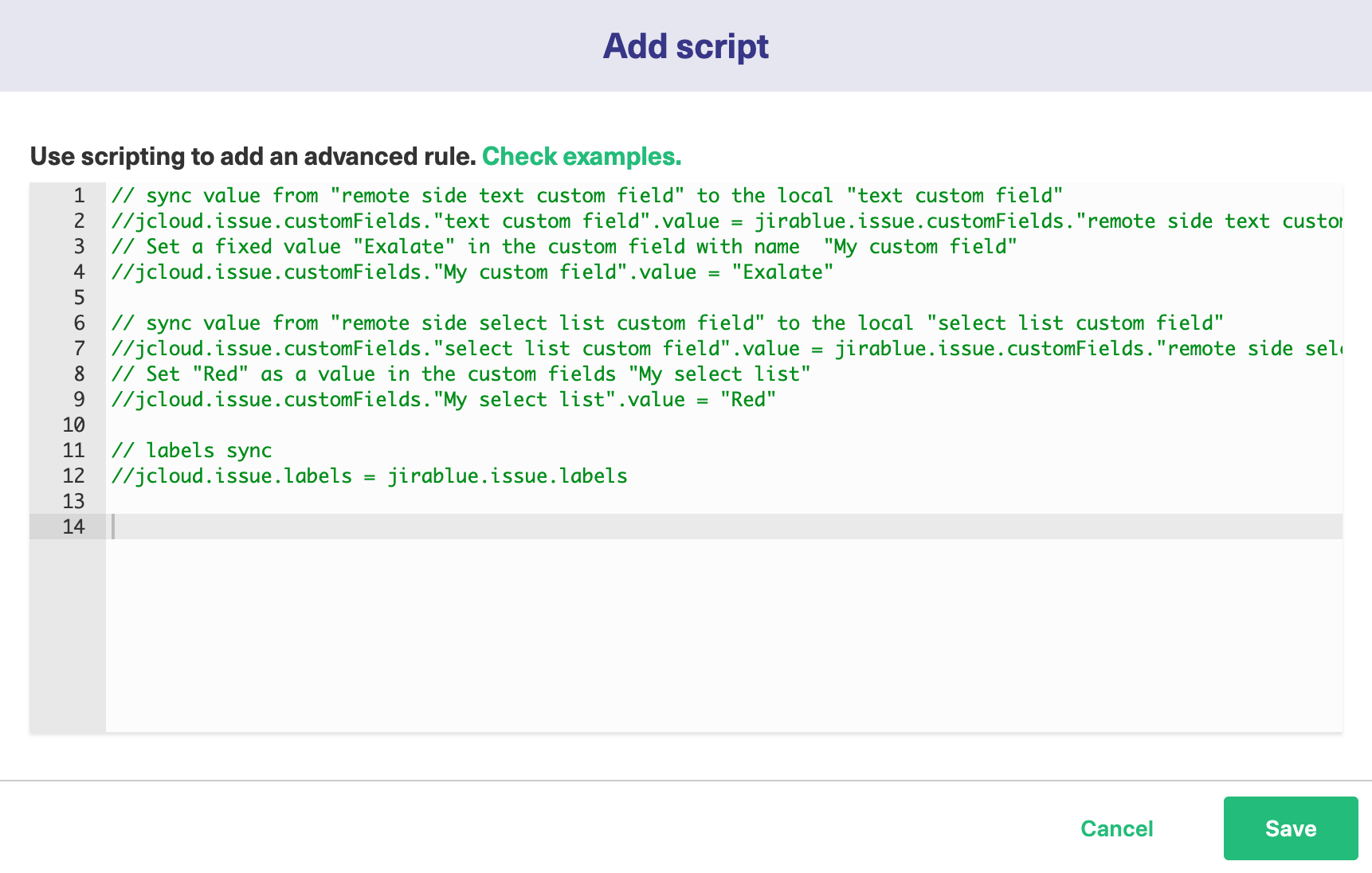
There is a default Script in the dialog box. You can edit it or simply delete the entire Script to start writing from scratch. Click Save when you finish adding the Scripts.
Script Syntax:
As a general rule of thumb, the Scripts follow the following syntax:
|
Where,
1. your_instance_shortname is the source instance.
2. remote_instance_shortname is the destination instance.
These are the names you provided while setting up the Connection.

3. This is followed by other issue properties, each separated with a "." operator.
Publish the Changes
To save the changes made to the Scope and Rules section and apply them to the Connection you have created, click Publish.
Note: You can also use these hotkeys to publish a connection:
- Ctrl+S on Windows or Linux
- Cmd+S on Mac
Note: Configuration changes made to the Connection are applied on the next synchronization.
What's Next?
Options you can consider next:
- If you have chosen to automatically start the synchronization in the Sync Scope, sit back and relax! Entities are synchronized based on the Scope Rules you have set.
- But if you want to set up an advanced automatic synchronization you can do so with Triggers.
- You can also read the Visual mode configuration guides.